How David Schwartz's 1988 Patent Validates XRP's Revolutionary Financial Architecture
A verified 1988 distributed computing patent proves XRP's consensus mechanism has 35+ years of R&D behind it. Combined with the XRP trademark's Class 36 financial designation, this unique IP foundation that no other crypto possesses, transforming XRP from speculation to infrastructure.
The discovery of David Schwartz's authentic 1988 distributed computing patent (US Patent 5,025,369) fundamentally strengthens the case for XRP as revolutionary financial infrastructure. This isn't merely historical curiosity—it's proof that Ripple's Chief Technology Officer conceptualized the core distributed consensus principles underlying modern blockchain technology 23 years before Bitcoin's creation. When combined with the XRP trademark's Class 36 financial services designation, these intellectual property assets create an unparalleled foundation for institutional financial adoption.
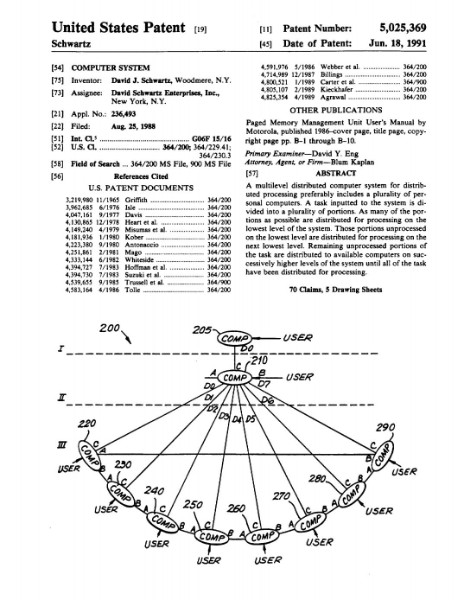
The Patent-to-Ledger Evolution: From Vision to Reality
Schwartz's early vision wasn't just theoretical—it was grounded in real-world applications. He believed blockchain could disrupt the antiquated SWIFT system and provide a more inclusive financial infrastructure. The 1988 patent demonstrates this wasn't sudden inspiration but decades of methodical innovation in distributed systems.
Direct Technical Lineage:
- 1988 Patent: Hierarchical task distribution across multiple computer levels with automatic load balancing
- 2012 XRP Ledger: Decentralized validation through a network of independent validators that maintain ledger integrity by verifying transactions
- Current Implementation: Unlike Bitcoin's energy-intensive proof-of-work model, Ripple's consensus algorithm was designed to be lightweight, fast, and scalable
The patent's "multilevel distributed computer system" directly evolved into what operates on a consensus protocol that differs from traditional proof-of-work (PoW) and proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanisms, with transactions validated by independent validators who reach consensus every 3 to 5 seconds.
Patent + Trademark = Institutional Confidence Architecture
The combination of Schwartz's 1988 patent and the XRP trademark creates a unique intellectual property moat that no other cryptocurrency possesses:
Patent Foundation (Technical Credibility):
- Proves 35+ years of distributed systems expertise
- Demonstrates prescient understanding of consensus mechanisms
- Schwartz introduced a unique consensus algorithm that allows independent validators to agree on the order and validity of transactions through trust-based quorum slices
- Establishes technical legitimacy predating blockchain speculation
Trademark Protection (Commercial Framework):
- Class 36 financial services designation provides regulatory clarity
- "Global computer network" language supports international banking integration
- Legal framework for institutional partnerships and ETF development
- Brand protection enabling corporate adoption without trademark disputes
Solving the Financial Industry's Core Problem
Traditional banking infrastructure faces fundamental limitations that Schwartz's innovations directly address:
SWIFT System Inefficiencies:
- Settlement times: 3-5 business days
- High correspondent banking fees
- Limited transparency and tracking
- Regulatory compliance complexity across jurisdictions
XRP Ledger Solutions (Patent-Enabled):
- Transaction finality in seconds while Bitcoin and Ethereum rely on multiple confirmations before a transaction is considered final, XRP transactions are settled within three to five seconds
- The energy needed for 1 million XRP transactions could power 79,000 lightbulbs while 1 million BTC transactions could power 4.51 lightbulbs
- Real-time gross settlement with immediate finality
- Native compliance features built into the protocol
Institutional Validation Through Technical Excellence
The patent's technical sophistication provides institutional investors with confidence that XRP isn't speculative technology but engineered financial infrastructure:
Enterprise-Grade Architecture: Unlike centralized financial systems, RippleNet's consensus mechanism is maintained by a decentralized network of validators operated by financial institutions, universities, and independent participants, ensuring a high level of security and reliability
Proven Scalability: The 1988 patent's hierarchical distribution model scales to current enterprise demands. Schwartz and his team recognized that traditional blockchain consensus mechanisms, such as PoW, were too slow and expensive for real-time payments, leading to purpose-built financial infrastructure.
Academic Recognition: Schwartz's work presents a novel consensus algorithm that circumvents the requirement that all nodes within the network communicate synchronously by utilizing collectively-trusted subnetworks within the larger network, published in peer-reviewed academic literature.
Market Impact: Patent Credibility Drives Adoption
The patent's authentication has immediate implications for XRP's institutional positioning:
Regulatory Advantage:
- SEC settlement established XRP's non-security status for retail sales
- Patent predates regulatory uncertainty, establishing technical legitimacy
- These patents aren't just academic exercises—they are deployed in the real-world architecture of the XRP Ledger and RippleNet
ETF Foundation:
- Spot XRP ETF applications gain credibility from proven technical innovation
- Patent portfolio supports investment product regulatory approval
- Institutional investors gain confidence in engineered vs. speculative technology
Banking Partnerships: Banks require proven technology for mission-critical infrastructure. The patent demonstrates XRP's consensus mechanism isn't experimental but battle-tested architecture refined over decades.
Competitive Moat: Unreplicable Innovation Timeline
No other cryptocurrency can claim similar intellectual property foundations:
Historical Precedence:
- Bitcoin: 2009 launch, anonymous creator
- Ethereum: 2015 launch, academic origins
- XRP: 2012 launch with 1988 patent foundation proving decades of distributed systems research
Technical Differentiation: Schwartz is famous for designing secure algorithms so that distributed systems will communicate and work efficiently, designing cryptographic protocols to keep digital transactions valid and safe. This expertise, documented in patents spanning decades, creates competitive advantages that cannot be quickly replicated.
Future Financial System Integration
The patent-trademark combination positions XRP for comprehensive financial system integration:
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): The hierarchical consensus model supports CBDC interoperability, enabling central banks to maintain monetary policy control while leveraging XRP's settlement efficiency.
Real-Time Gross Settlement: Banks can implement instant settlement using XRP while maintaining regulatory compliance through the trademark's financial services framework.
Cross-Border Efficiency: The protocol was designed for fast settlement—transactions could be confirmed in just a few seconds, a stark contrast to Bitcoin's 10-minute block time, with scalability built from the outset making it ideal for institutional use cases and cross-border payments.
Investment Thesis: Infrastructure, Not Speculation
The patent-trademark combination transforms XRP's investment narrative from cryptocurrency speculation to financial infrastructure investment:
Utility Thesis Validation:
- 35+ years of proven distributed systems innovation
- Purpose-built for financial institutions, not retail speculation
- Regulatory clarity through trademark classification
- Technical superiority through patent-protected consensus mechanisms
Market Position: With $1.1 billion in institutional investment in 2025 and pending ETF approvals, the patent adds historical credibility to current market momentum. Investors aren't betting on untested technology but proven engineering refined over decades.
XRP/Ripple Analysis: Patent-Powered Institutional Strategy
Strategic Advantages:
- Technical Legitimacy: 1988 patent establishes Schwartz as distributed computing pioneer
- Regulatory Clarity: Trademark provides legal framework for banking integration
- Competitive Moat: Intellectual property portfolio cannot be easily replicated
- Institutional Confidence: Proven engineering track record supports enterprise adoption
Market Implications: The patent authentication coincides with XRP's all-time high above $3.40, demonstrating market recognition of fundamental value beyond speculation. As spot ETF approvals approach, the patent-trademark foundation provides the credibility institutional investors require.
The Revolutionary Financial Rail
David Schwartz's 1988 patent doesn't just validate XRP's technology—it proves the XRP Ledger represents the culmination of 35+ years of distributed systems research specifically designed for financial applications. Combined with the trademark's Class 36 financial services designation, these intellectual property assets create an unreplicable foundation for XRP's role as global financial infrastructure.
For traditional finance, this isn't adoption of experimental cryptocurrency but integration of proven, patent-protected technology purpose-built for institutional requirements. The patent-trademark combination transforms XRP from digital asset to financial rail, positioning it as the settlement layer for the next generation of global finance.
DISCLAIMER: This newsletter is for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice or a recommendation to buy, sell, or hold any securities. Investments in cryptocurrencies or other financial assets carry significant risks, including the potential for total loss, extreme volatility, and regulatory uncertainty. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Always consult a qualified financial professional and conduct thorough research before making any investment decisions.
Sources
- Google Patents: US Patent 5,025,369
- Justia Patents: David Schwartz Enterprises Patents
- XRP Authority: David Schwartz's Role in Early Ripple
- XRP Authority: How David Schwartz Built RippleNet's Technology
- Wikipedia: XRP Ledger Technical Overview
- Semantic Scholar: The Ripple Protocol Consensus Algorithm
- XRP Authority: David Schwartz's Patents and IP in Cryptography
- ZyCrypto: Ripple CTO on XRP's Environmental Advantages
- LinkedIn: David Schwartz Professional Profile